Description
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a
height-balanced
binary search tree.
Example 1:
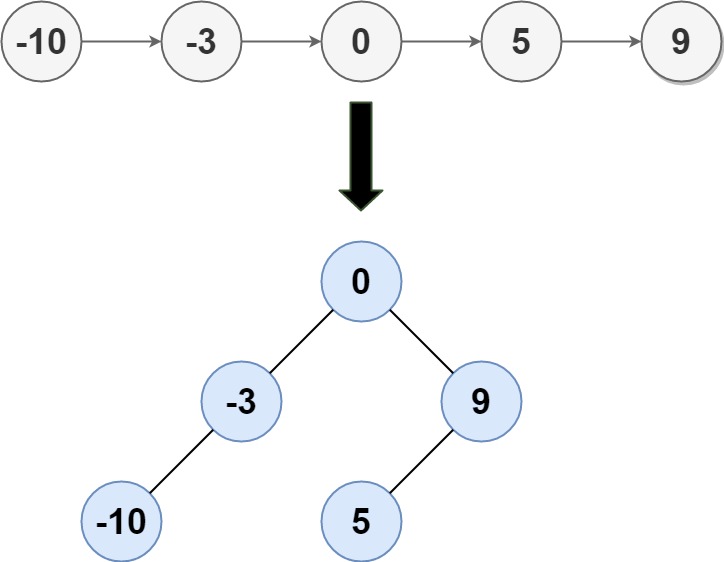
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9] Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5] Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
Example 2:
Input: head = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in
headis in the range[0, 2 * 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Code
概念同 Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree,只是從 array 換成 linked list,因此找中點要用 slow fast pointer。
概念也有點像 Sort List 中用到的 merge sort。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
if(!head) return nullptr;
if(!head->next) {
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(head->val);
return node;
}
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* prev = head;
while(fast && fast->next) {
prev = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
// slow is mid
prev->next = nullptr;
TreeNode* mid = new TreeNode(slow->val);
mid->right = sortedListToBST(slow->next);
mid->left = sortedListToBST(head);
return mid;
}
};