Description
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
Example 1:
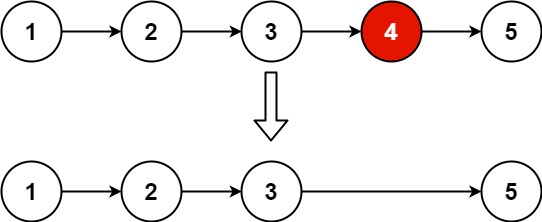
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1], n = 1 Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1 Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
sz. 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
Follow up: Could you do this in one pass?
Code
Indirect Pointer
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
Since we’re using indirect pointer, there is no edge case that needs to be dealt with!
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n) {
struct ListNode** slow = &head;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast) {
slow = &((*slow)->next);
fast = fast->next;
}
*slow = (*slow)->next;
return head;
}Pointer
Edge Case: Example 3.
處理:if (!fast) return head->next;
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
fast = fast->next;
}
if (!fast) return head->next;
ListNode* prev = head;
while(fast) {
prev = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
// now slow is the target
prev->next = slow->next;
return head;
}
};