Description
We have n jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from startTime[i] to endTime[i], obtaining a profit of profit[i].
You’re given the startTime, endTime and profit arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
If you choose a job that ends at time X you will be able to start another job that starts at time X.
Example 1:
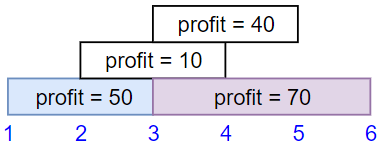
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70] Output: 120 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first and fourth job. Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
Example 2:
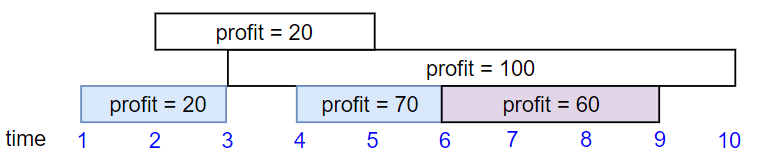
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60] Output: 150 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job. Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
Example 3:
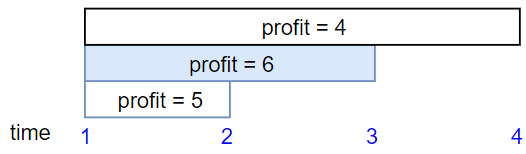
Input: startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4] Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 1041 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 1091 <= profit[i] <= 104
Code
在 Maximum Length of Pair Chain 中我們可以使用 Greedy,但這裡每個 interval 具有 weight(profit),因此要用 DP。
DP
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
vector<vector<int>> T;
int n = startTime.size();
// base case
T.push_back({0, 0, 0});
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
T.push_back({endTime[i], startTime[i], profit[i]});
}
sort(T.begin(), T.end());
n = T.size();
int dp[n];
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(i == 0) {
dp[i] = T[i][2];
continue;
}
dp[i] = dp[i-1];
int startTime = T[i][1];
int profit = T[i][2];
for(int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
int endTime = T[j][0];
if(endTime <= startTime) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + profit);
break;
}
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
};DP + Binary Search
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
vector<vector<int>> jobs;
int n = startTime.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
jobs.push_back({endTime[i], startTime[i], profit[i]});
}
sort(jobs.begin(), jobs.end());
map<int, int> dp = {{0, 0}}; // base case
for(auto &job: jobs) {
int cur = prev(dp.upper_bound(job[1]))->second + job[2]; // binary search
if(cur > dp.rbegin()->second) {
dp[job[0]] = cur;
}
}
return dp.rbegin()->second;
}
};