Description
There are n computers numbered from 0 to n - 1 connected by ethernet cables connections forming a network where connections[i] = [ai, bi] represents a connection between computers ai and bi. Any computer can reach any other computer directly or indirectly through the network.
You are given an initial computer network connections. You can extract certain cables between two directly connected computers, and place them between any pair of disconnected computers to make them directly connected.
Return the minimum number of times you need to do this in order to make all the computers connected. If it is not possible, return -1.
Example 1:
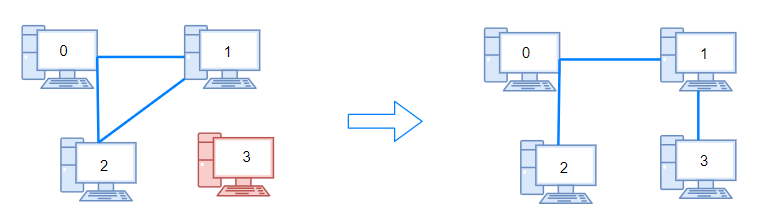
Input: n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2]] Output: 1 Explanation: Remove cable between computer 1 and 2 and place between computers 1 and 3.
Example 2:
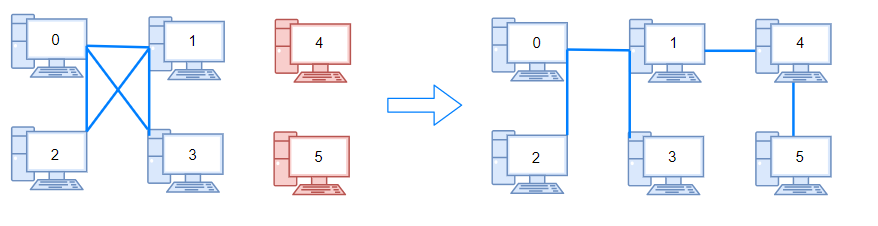
Input: n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,2],[1,3]] Output: 2
Example 3:
Input: n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,2]] Output: -1 Explanation: There are not enough cables.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1051 <= connections.length <= min(n * (n - 1) / 2, 105)connections[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bi- There are no repeated connections.
- No two computers are connected by more than one cable.
Code
經典 disjoint set 的題目,類似 Redundant Connection。
Union and Find
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
class Solution {
public:
int makeConnected(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
int n_edges = connections.size();
if(n_edges < n - 1) return -1;
vector<int> parent(n, 0);
vector<int> size(n , 1);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
int non_connected = n;
for(auto& conn: connections) {
int p1 = find(conn[0], parent);
int p2 = find(conn[1], parent);
if(p1 != p2) {
if(size[p1] < size[p2]) {
parent[p1] = p2;
size[p2] += size[p1];
} else {
parent[p2] = p1;
size[p1] += size[p2];
}
non_connected--;
}
}
return non_connected - 1;
}
int find(int idx, vector<int>& parent) {
return parent[idx] = parent[idx] == idx ? idx : find(parent[idx], parent);
}
};class Solution {
unordered_map<int, int> f;
int component;
public:
int makeConnected(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
if(connections.size() < n - 1) return -1;
component = n;
for(int i = 0; i < connections.size(); i++) {
uni(connections[i][0], connections[i][1]);
}
return component - 1;
}
int find(int x) {
if(!f.count(x)) {
f[x] = x;
}
if(f[x] != x) {
f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
return f[x];
}
void uni(int x, int y) {
x = find(x), y = find(y);
if(x != y) {
f[x] = y;
component--;
}
}
};