Description
You are given an undirected weighted graph of n nodes (0-indexed), represented by an edge list where edges[i] = [a, b] is an undirected edge connecting the nodes a and b with a probability of success of traversing that edge succProb[i].
Given two nodes start and end, find the path with the maximum probability of success to go from start to end and return its success probability.
If there is no path from start to end, return 0. Your answer will be accepted if it differs from the correct answer by at most 1e-5.
Example 1:
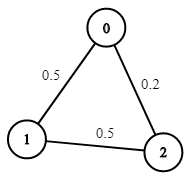
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.2], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.25000 Explanation: There are two paths from start to end, one having a probability of success = 0.2 and the other has 0.5 * 0.5 = 0.25.
Example 2:
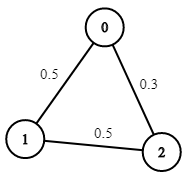
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.3], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.30000
Example 3:
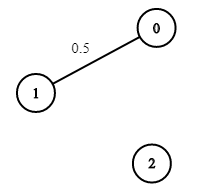
Input: n = 3, edges = 0,1, succProb = [0.5], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.00000 Explanation: There is no path between 0 and 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10^40 <= start, end < nstart != end0 <= a, b < na != b0 <= succProb.length == edges.length <= 2*10^40 <= succProb[i] <= 1- There is at most one edge between every two nodes.
Code
To maximize is the same as to minimize , and , that means, we can transform the probability of a edge into and the find the shortest path from source to destination, and then transform the shortest path weight back as the returned answer.
Bellman-Ford (TLE)
Time Complexity:
因為是 undirected graph,所以對 input 的每一個 edge relax 兩次!
class Solution {
public:
double maxProbability(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<double>& succProb, int start_node, int end_node) {
vector<double> dp(n, 1e5);
dp[start_node] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
vector<double> temp(dp);
for(int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
double p = succProb[i];
double pp = -(double)log2(p);
int u = edges[i][0], v = edges[i][1];
if(dp[u] == INT_MAX) continue;
temp[v] = min(temp[v], dp[u] + pp);
v = edges[i][0], u = edges[i][1];
if(dp[u] == INT_MAX) continue;
temp[v] = min(temp[v], dp[u] + pp);
}
dp = temp;
}
if(dp[end_node] == 1e5) return 0;
auto real_p = pow(2, -dp[end_node]);
return real_p;
}
};Dijkstra
Time Complexity:
class Solution {
public:
double maxProbability(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<double>& succProb, int start_node, int end_node) {
vector<vector<pair<int, double>>> adj(n);
for(int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
double p = succProb[i];
double p_transform = -(double)log2(p);
int u = edges[i][0], v = edges[i][1];
adj[u].push_back({v, p_transform});
adj[v].push_back({u, p_transform});
}
// min heap
auto cmp = [](const pair<int, double>& p1, const pair<int, double>& p2){
return p1.second > p2.second;
};
priority_queue<pair<int, double>, vector<pair<int, double>>, decltype(cmp)> pq(cmp);
pq.push({start_node, 0});
vector<double> dp(n, 1e5);
dp[start_node] = 0;
while(!pq.empty()) {
auto node = pq.top(); pq.pop();
int u = node.first;
double cost = node.second;
for(int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++) {
int v = adj[u][i].first;
double w = adj[u][i].second;
if(cost + w < dp[v]) {
dp[v] = cost + w;
pq.push({v, dp[v]});
}
}
}
if(dp[end_node] == 1e5) return 0;
auto real_p = pow(2, -dp[end_node]);
return real_p;
}
};