Description
Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a “linked list”:
- The “linked list” should use the same
TreeNodeclass where therightchild pointer points to the next node in the list and theleftchild pointer is alwaysnull. - The “linked list” should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
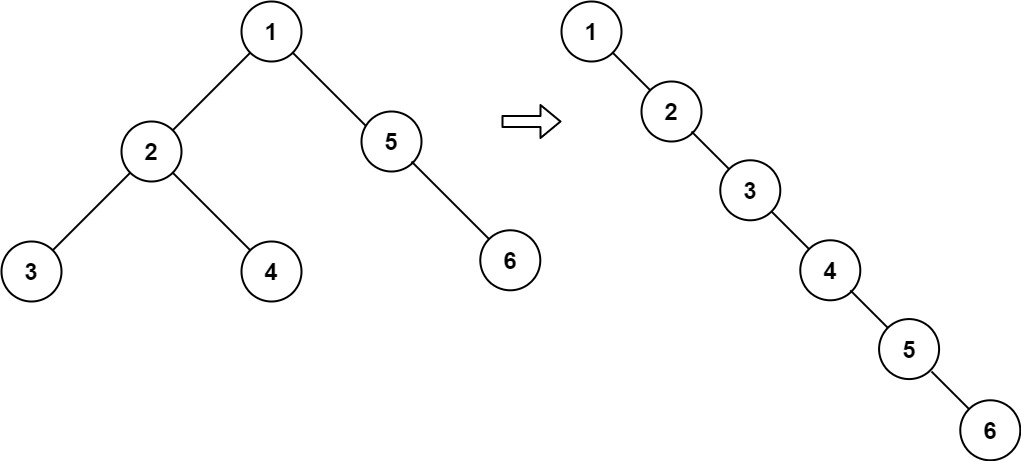
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [0] Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Can you flatten the tree in-place (with O(1) extra space)?
Code
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
神解法。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
if(root) {
auto tmp = root->right;
root->right = root->left;
root->left = nullptr;
auto node = root;
while(node->right)
node = node->right;
node->right = tmp;
flatten(root->right);
}
}
};