Description
You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes. Each node is assigned a unique value from 1 to n. You are also given an array queries of size m.
You have to perform m independent queries on the tree where in the ith query you do the following:
- Remove the subtree rooted at the node with the value
queries[i]from the tree. It is guaranteed thatqueries[i]will not be equal to the value of the root.
Return an array answer of size m where answer[i] is the height of the tree after performing the ith query.
Note:
- The queries are independent, so the tree returns to its initial state after each query.
- The height of a tree is the number of edges in the longest simple path from the root to some node in the tree.
Example 1:
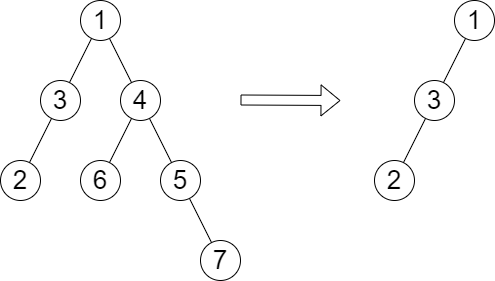
Input: root = [1,3,4,2,null,6,5,null,null,null,null,null,7], queries = [4] Output: [2] Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree after removing the subtree rooted at node with value 4. The height of the tree is 2 (The path 1 → 3 → 2).
Example 2:
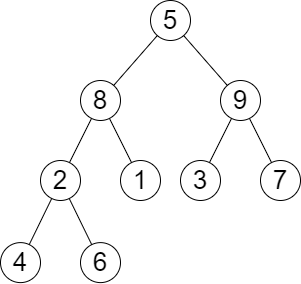
Input: root = [5,8,9,2,1,3,7,4,6], queries = [3,2,4,8] Output: [3,2,3,2] Explanation: We have the following queries:
- Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 3. The height of the tree becomes 3 (The path 5 → 8 → 2 → 4).
- Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 2. The height of the tree becomes 2 (The path 5 → 8 → 1).
- Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 4. The height of the tree becomes 3 (The path 5 → 8 → 2 → 6).
- Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 8. The height of the tree becomes 2 (The path 5 → 9 → 3).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 2 <= n <= 1051 <= Node.val <= n- All the values in the tree are unique.
m == queries.length1 <= m <= min(n, 104)1 <= queries[i] <= nqueries[i] != root.val
Code
Thinking Process:
- 每一次 query,暴力解都是重新從 root traverse 一次,就可得到答案
- 是否可以 pre compute?可以,height 和 depth 都可以,兩者合起來就是答案
- 面對一個 query ,誰會是 candidate node?就是該 node 的 cousins(所有同 depth 的 node)
- 是否還有 optimize 的空間?有,我們只會需要至多一個該 node 的替代人選
TLE 版本(how to optimize ? 我們只會需要至多一個該 node 的替代人選)
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> cousins;
unordered_map<int, int> depth;
unordered_map<int, int> height;
vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {
int _ = dfs(root, 0); // build depth and height;
// build cousins
for(auto [node, d]: depth) {
cousins[d].push_back(node);
}
vector<int> res;
for(auto & q: queries) {
int curr_depth = depth[q];
int curr_h = curr_depth - 1;
for(auto & c: cousins[curr_depth]) {
if (c == q) {
continue;
}
curr_h = max(curr_h, depth[c] + height[c] - 1);
}
res.push_back(curr_h);
}
return res;
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root, int level) {
if(!root) {
return 0;
}
depth[root->val] = level;
auto l = dfs(root->left, level + 1);
auto r = dfs(root->right, level + 1);
return height[root->val] = max(l, r) + 1;
}
};Optimal Solution
差別只在於原本的 unordered_map<int, vector<int>> cousins; 裝的是一個 node 對應的所有 cousin 的 node index,現在, unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int, int>>> cousins; 裝的是一個 node 對應的所有 cousin 的 height 和 node index ,且必須保持 height 是 sorted,size 不超過 2。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int, int>>> cousins;
unordered_map<int, int> depth;
unordered_map<int, int> height;
vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {
int _ = dfs(root, 0); // build depth and height;
// build cousins
for(auto [node, d]: depth) {
cousins[d].push_back({height[node], node});
sort(begin(cousins[d]), end(cousins[d]), greater<pair<int, int>>());
if(cousins[d].size() > 2) {
cousins[d].pop_back();
}
}
vector<int> res;
for(auto & q: queries) {
int curr_depth = depth[q];
int curr_h = curr_depth - 1;
for(auto & [h, c]: cousins[curr_depth]) {
if (c == q) {
continue;
}
curr_h = max(curr_h, depth[c] + h - 1);
}
res.push_back(curr_h);
}
return res;
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root, int level) {
if(!root) {
return 0;
}
depth[root->val] = level;
auto l = dfs(root->left, level + 1);
auto r = dfs(root->right, level + 1);
return height[root->val] = max(l, r) + 1;
}
};