Description
There is a one-dimensional garden on the x-axis. The garden starts at the point 0 and ends at the point n. (i.e., the length of the garden is n).
There are n + 1 taps located at points [0, 1, ..., n] in the garden.
Given an integer n and an integer array ranges of length n + 1 where ranges[i] (0-indexed) means the i-th tap can water the area [i - ranges[i], i + ranges[i]] if it was open.
Return the minimum number of taps that should be open to water the whole garden, If the garden cannot be watered return -1.
Example 1:
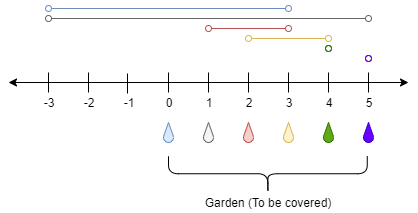
Input: n = 5, ranges = [3,4,1,1,0,0] Output: 1 Explanation: The tap at point 0 can cover the interval [-3,3] The tap at point 1 can cover the interval [-3,5] The tap at point 2 can cover the interval [1,3] The tap at point 3 can cover the interval [2,4] The tap at point 4 can cover the interval [4,4] The tap at point 5 can cover the interval [5,5] Opening Only the second tap will water the whole garden [0,5]
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, ranges = [0,0,0,0] Output: -1 Explanation: Even if you activate all the four taps you cannot water the whole garden.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 104ranges.length == n + 10 <= ranges[i] <= 100
Code
和 Video Stitching 、Jump Game II 一樣的解法。
DP
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
在這題中不需要 Sorting,因為 ranges 本身就是按照 index 排序好的。
DP[i]: minimum no. of taps required to water the region from 0 to i (both inclusive)
class Solution {
public:
int minTaps(int n, vector<int>& ranges) {
int len = ranges.size();
int dp[len + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < len + 1; i++) {
dp[i] = len + 1;
}
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int start = max(0, i - ranges[i]);
int end = min(len - 1, i + ranges[i]);
for(int j = start; j <= end; j++) {
dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[start] + 1);
}
}
return dp[len - 1] == len + 1 ? -1 : dp[len - 1];
}
};
Greedy
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
class Solution {
public:
int minTaps(int n, vector<int>& ranges) {
unordered_map<int, int> range_map;
for(int i = 0; i < ranges.size(); i++) {
int start = max(0, i - ranges[i]);
int end = min(n, i + ranges[i]);
range_map[start] = max(range_map[start], end);
}
int prev_covered = -1, covered = 0, count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if(covered >= n || i > covered) break;
if(range_map.count(i)) {
if(i > prev_covered) {
count++;
prev_covered = covered;
}
covered = max(covered, range_map[i]);
}
}
return covered >= n ? count : -1;
}
};