Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the leftmost value in the last row of the tree.
Example 1:
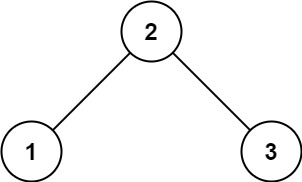
Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: 1
Example 2:
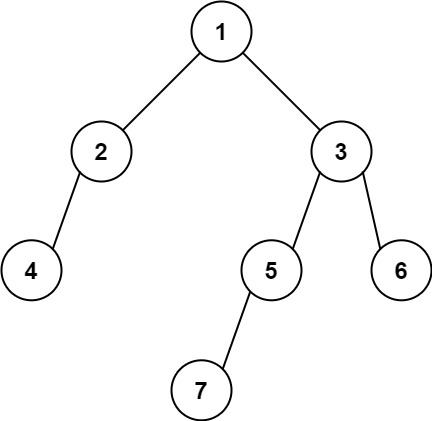
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7] Output: 7
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Code
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
From left to right:
使用 Binary Tree Level Order Traversal,若是由左到右,則用 firstLeft 去紀錄每一層的最左邊的 node。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
TreeNode* firstLeft = nullptr;
while(!q.empty()) {
int n = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
auto child = q.front();
if(i == 0) firstLeft = child;
q.pop();
if(child->left) q.push(child->left);
if(child->right) q.push(child->right);
}
}
return firstLeft->val;
}
};若是由右到左,就不需要額外的 pointer 了。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
int n = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
root = q.front();
q.pop();
if(root->right) q.push(root->right);
if(root->left) q.push(root->left);
}
}
return root->val;
}
};