Description
There is a pizza with 3n slices of varying size, you and your friends will take slices of pizza as follows:
- You will pick any pizza slice.
- Your friend Alice will pick the next slice in the anti-clockwise direction of your pick.
- Your friend Bob will pick the next slice in the clockwise direction of your pick.
- Repeat until there are no more slices of pizzas.
Given an integer array slices that represent the sizes of the pizza slices in a clockwise direction, return the maximum possible sum of slice sizes that you can pick.
Example 1:
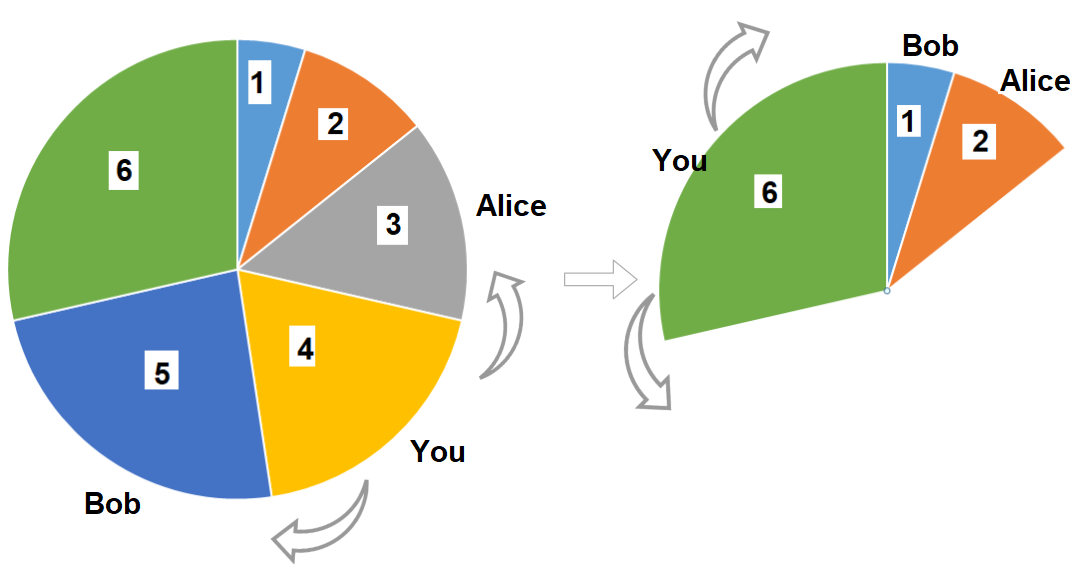
Input: slices = [1,2,3,4,5,6] Output: 10 Explanation: Pick pizza slice of size 4, Alice and Bob will pick slices with size 3 and 5 respectively. Then Pick slices with size 6, finally Alice and Bob will pick slice of size 2 and 1 respectively. Total = 4 + 6.
Example 2:
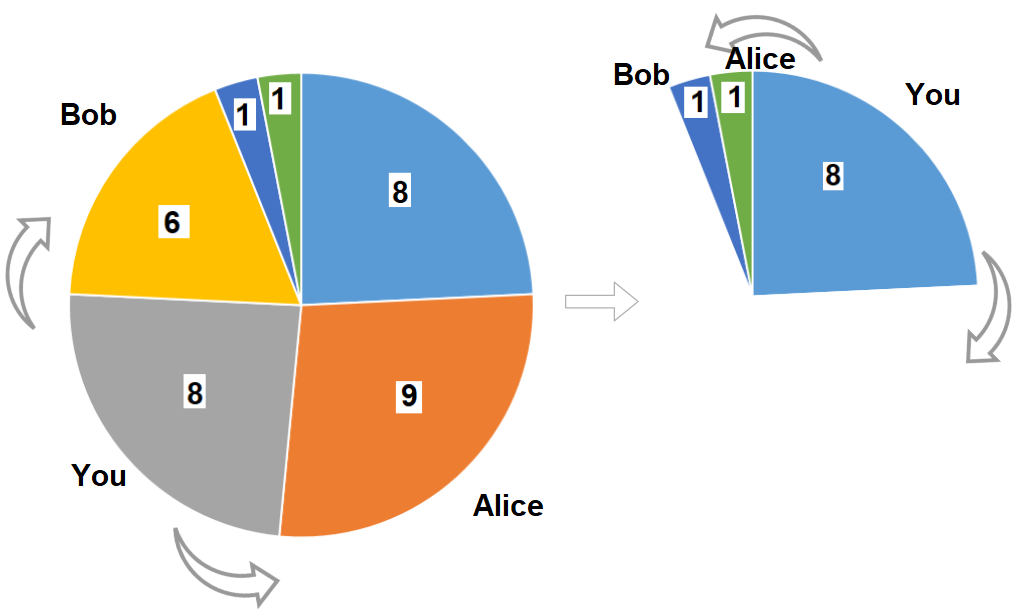
Input: slices = [8,9,8,6,1,1] Output: 16 Explanation: Pick pizza slice of size 8 in each turn. If you pick slice with size 9 your partners will pick slices of size 8.
Constraints:
3 * n == slices.length1 <= slices.length <= 5001 <= slices[i] <= 1000
Code
Brute Force - TLE
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
class Solution {
int res = INT_MIN;
public:
int maxSizeSlices(vector<int>& slices) {
unordered_set<int> used;
solve(slices, 0, used);
return res;
}
void solve(vector<int>& slices, int sum, unordered_set<int>& used) {
if(used.size() == slices.size()) {
res = max(res, sum);
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < slices.size(); i++) {
if(!used.count(i)) {
int alice = i;
while(used.size() < slices.size()) {
alice = ((alice - 1) + slices.size()) % slices.size();
if(!used.count(alice)) break;
}
int bob = i;
while(used.size() < slices.size()) {
bob = (bob + 1) % slices.size();
if(!used.count(bob)) break;
}
used.insert(i);
used.insert(alice);
used.insert(bob);
solve(slices, sum + slices[i], used);
used.erase(i);
used.erase(alice);
used.erase(bob);
}
}
}
};但是這個解法的 memoization 不知道該從何下手。
DP with memoization
Intuition:House Robber II。
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
class Solution {
int memo[501][170];
public:
int maxSizeSlices(vector<int>& slices) {
int n = slices.size();
// ignore the first one
memset(memo, -1, sizeof(memo));
int p1 = solve(1, n / 3, slices);
// ignore the last one
memset(memo, -1, sizeof(memo));
slices[n-1] = 0;
int p2 = solve(0, n / 3, slices);
return max(p1, p2);
}
int solve(int i, int n, vector<int>& slices) {
if(i >= slices.size() || n == 0) return 0;
if(memo[i][n] != -1) return memo[i][n];
return memo[i][n] = max(solve(i + 1, n, slices), slices[i] + solve(i + 2, n - 1, slices));
}
};