Description
Given a matrix and a target, return the number of non-empty submatrices that sum to target.
A submatrix x1, y1, x2, y2 is the set of all cells matrix[x][y] with x1 <= x <= x2 and y1 <= y <= y2.
Two submatrices (x1, y1, x2, y2) and (x1', y1', x2', y2') are different if they have some coordinate that is different: for example, if x1 != x1'.
Example 1:
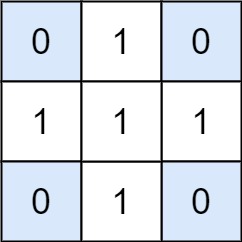
Input: matrix = [[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]], target = 0 Output: 4 Explanation: The four 1x1 submatrices that only contain 0.
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [[1,-1],[-1,1]], target = 0 Output: 5 Explanation: The two 1x2 submatrices, plus the two 2x1 submatrices, plus the 2x2 submatrix.
Example 3:
Input: matrix = 904, target = 0 Output: 0
Constraints:
1 <= matrix.length <= 1001 <= matrix[0].length <= 100-1000 <= matrix[i] <= 1000-10^8 <= target <= 10^8
Code
Subarray Sum Equals K 的 2D 版本。
和 Subarray Sum Equals K 中的概念相同,只要目前為止的 prefixSum 減去 k 之後的值是有出現過的,代表從目前這個位置,到之前有出現過的位置(可能有多個),中間的 subarray 其 sum 都等於 k。
res += mp[prefixSum[i] - k];因此在這題中,我們有以下的程式碼:
res += counter.find(cur - target) != counter.end() ? counter[cur - target] : 0;Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
class Solution {
public:
int numSubmatrixSumTarget(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++)
matrix[i][j] += matrix[i][j - 1];
// i, j for col combinations
// k for row index
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = i; j < n; j++) {
unordered_map<int, int> count = {{0, 1}};
int curSum = 0;
for(int k = 0; k < m; k++) {
curSum += matrix[k][j] - (i > 0 ? matrix[k][i - 1] : 0);
if(count.find(curSum - target) != count.end()) {
res += count[curSum - target];
}
count[curSum]++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};