Description
Given an integer array nums, handle multiple queries of the following types:
- Update the value of an element in
nums. - Calculate the sum of the elements of
numsbetween indicesleftandrightinclusive whereleft <= right.
Implement the NumArray class:
NumArray(int[] nums)Initializes the object with the integer arraynums.void update(int index, int val)Updates the value ofnums[index]to beval.int sumRange(int left, int right)Returns the sum of the elements ofnumsbetween indicesleftandrightinclusive (i.e.nums[left] + nums[left + 1] + ... + nums[right]).
Example 1:
<strong>Input</strong>
["NumArray", "sumRange", "update", "sumRange"]
[[[1, 3, 5]], [0, 2], [1, 2], [0, 2]]
<strong>Output</strong>
[null, 9, null, 8]
<strong>Explanation</strong>
NumArray numArray = new NumArray([1, 3, 5]);
numArray.sumRange(0, 2); // return 1 + 3 + 5 = 9
numArray.update(1, 2); // nums = [1, 2, 5]
numArray.sumRange(0, 2); // return 1 + 2 + 5 = 8
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 10<sup>4</sup>-100 <= nums[i] <= 1000 <= index < nums.length-100 <= val <= 1000 <= left <= right < nums.length- At most
3 * 10<sup>4</sup>calls will be made toupdateandsumRange.
Code
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
segment tree 背後的精神是 divide and conquer。
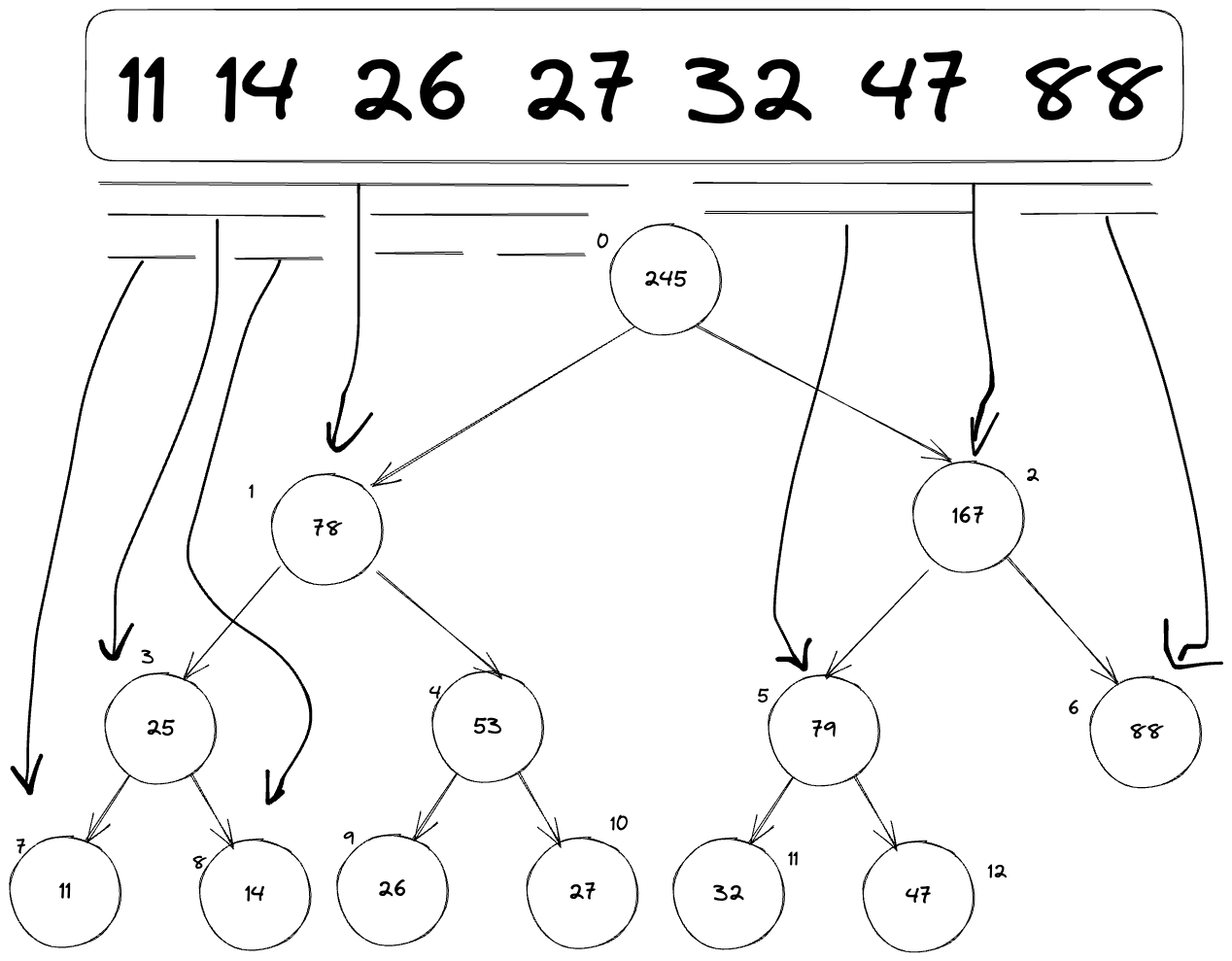
用原本的 array 的 left right mid 去做 divide and conquer,而 index parameter 是 for segment tree array 使用的,更新方式是 left child = 2 index + 1, right child = 2 index + 2(zero based)。
#define lc 2 * index + 1
#define rc 2 * index + 2
class NumArray {
vector<int> A;
vector<int> S;
public:
int buildTree(int left, int right, int index) {
if(left == right)
return S[index] = A[left];
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
return S[index] = buildTree(left, mid, lc) + buildTree(mid + 1, right, rc);
}
void updateTree(int t, int left, int right, int index, int data) {
if(t < left || t > right) return;
if(left == t && right == t) {
S[index] = data;
return;
}
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
updateTree(t, left, mid, lc, data);
updateTree(t, mid + 1, right, rc, data);
S[index] = S[lc] + S[rc];
}
int query(int qleft, int qright, int left, int right, int index) {
if(qleft > right || qright < left) return 0;
else if(qleft <= left && right <= qright) return S[index];
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
return query(qleft, qright, left, mid, lc) + query(qleft, qright, mid + 1, right, rc);
}
NumArray(vector<int>& nums) {
A = nums;
int n = A.size();
S.resize(4*n);
buildTree(0, n - 1, 0);
}
void update(int index, int val) {
updateTree(index, 0, A.size() - 1, 0, val);
}
int sumRange(int left, int right) {
return query(left, right, 0, A.size() - 1, 0);
}
};
/**
* Your NumArray object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NumArray* obj = new NumArray(nums);
* obj->update(index,val);
* int param_2 = obj->sumRange(left,right);
*/