Description
Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
Example 1:
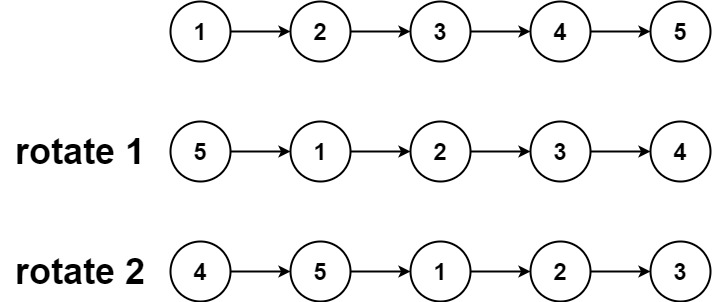
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2:
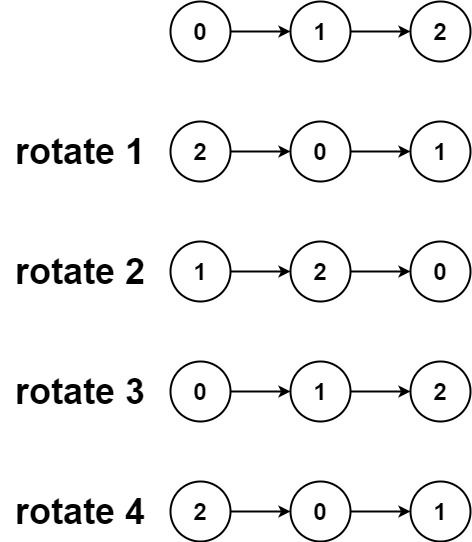
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4 Output: [2,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 500]. -100 <= Node.val <= 1000 <= k <= 2 * 109
Code
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
思路:找到 rotate 後的起點,再將 linked list 串起來變成 circular linked list,最後再找到新的 head 之前的點,斷開即可。
使用 int newHeadIndex = listNum - k % listNum; 即可找出新的 head 在哪裏。
串起來變成 circular linked list 的好處在於,可以避免掉 edge case,因次 linked list 自始至終都是串在一起的,沒有存取 null pointer 的問題。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* rotateRight(struct ListNode* head, int k) {
if(!head) return NULL;
int n = 1;
struct ListNode* tail = head;
while(tail->next) {
n++;
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = head;
k = n - k % n;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
tail = tail->next;
}
head = tail->next;
tail->next = NULL;
return head;
}class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head == null) return null;
int listNum = 1;
ListNode tail = head;
//find tail and count listNum
while(tail.next != null){
listNum++;
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = head;
int newHeadIndex = listNum - k % listNum;
for(int i = 0; i < newHeadIndex; i++){
tail = tail.next;
}
head = tail.next;
tail.next = null;
return head;
}
}``