Description
You have n flower seeds. Every seed must be planted first before it can begin to grow, then bloom. Planting a seed takes time and so does the growth of a seed. You are given two 0-indexed integer arrays plantTime and growTime, of length n each:
plantTime[i]is the number of full days it takes you to plant theithseed. Every day, you can work on planting exactly one seed. You do not have to work on planting the same seed on consecutive days, but the planting of a seed is not complete until you have workedplantTime[i]days on planting it in total.growTime[i]is the number of full days it takes theithseed to grow after being completely planted. After the last day of its growth, the flower blooms and stays bloomed forever.
From the beginning of day 0, you can plant the seeds in any order.
Return the earliest possible day where all seeds are blooming.
Example 1:
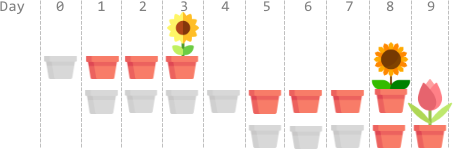
Input: plantTime = [1,4,3], growTime = [2,3,1] Output: 9 Explanation: The grayed out pots represent planting days, colored pots represent growing days, and the flower represents the day it blooms. One optimal way is: On day 0, plant the 0th seed. The seed grows for 2 full days and blooms on day 3. On days 1, 2, 3, and 4, plant the 1st seed. The seed grows for 3 full days and blooms on day 8. On days 5, 6, and 7, plant the 2nd seed. The seed grows for 1 full day and blooms on day 9. Thus, on day 9, all the seeds are blooming.
Example 2:
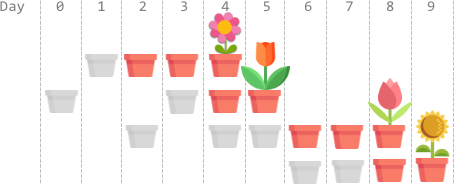
Input: plantTime = [1,2,3,2], growTime = [2,1,2,1] Output: 9 Explanation: The grayed out pots represent planting days, colored pots represent growing days, and the flower represents the day it blooms. One optimal way is: On day 1, plant the 0th seed. The seed grows for 2 full days and blooms on day 4. On days 0 and 3, plant the 1st seed. The seed grows for 1 full day and blooms on day 5. On days 2, 4, and 5, plant the 2nd seed. The seed grows for 2 full days and blooms on day 8. On days 6 and 7, plant the 3rd seed. The seed grows for 1 full day and blooms on day 9. Thus, on day 9, all the seeds are blooming.
Example 3:
Input: plantTime = [1], growTime = [1] Output: 2 Explanation: On day 0, plant the 0th seed. The seed grows for 1 full day and blooms on day 2. Thus, on day 2, all the seeds are blooming.
Constraints:
n == plantTime.length == growTime.length1 <= n <= 1051 <= plantTime[i], growTime[i] <= 104
Code
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
Greedy Choice: largest grow time first
使用 Greedy Algorithm 中的證明方法來證明此 greedy choice 會為我們帶來 global optimal solution。
Claim:存在一個包含 greedy choice 的 Optimal Solution。
- 若 greedy choice 的確被包含在此 Optimal Solution 中,則證明完畢。
- 若 greedy choice 不被包含,則我們要將其中一個 choice 換成 greedy choice,得到一個新的 Solution。
若此 Solution 比原本的好,就代表原本的 Optimal Solution 並不 optimal,因此包含 greedy choice 的解才是 Optimal Solution。
若新的 Solution 和原本的一樣好,那就代表新的 Solution 也是 Optimal Sollution,因此存在一個 Optimal Solution 包含 greedy choice,因此用 greedy algorithm 可以得到最佳解。
以 plantTime = [1,2,3,2], growTime = [2,1,2,1] 為例,Optimal Solution 就是(0 代表 plantTime,1 代表 growTime):
0 1 1 1
0 0 1 1
0 0 0 1 1 1
0 0 1 1此解包含 greedy choice,因此是 Optimal Solution。
考慮以下這個 Solution,我們可以將三四行的 choices 換成 greedy choice,得到的解會比原本的好,因此使用 greedy choice 可以得到 Optimal Solution。
0 1 1 1
0 0 1 1
0 0 1 1
0 0 0 1 1 1class Solution {
public:
int earliestFullBloom(vector<int>& plantTime, vector<int>& growTime) {
int n = plantTime.size();
vector<pair<int, int>> t;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
t.push_back({-growTime[i], plantTime[i]});
}
sort(t.begin(), t.end());
int res = 0;
int plantEnd = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
plantEnd += t[i].second;
res = max(res, plantEnd + -t[i].first);
}
return res;
}
};