Description
You are given the head of a linked list, and an integer k.
Return the head of the linked list after swapping the values of the kth node from the beginning and the kth node from the end (the list is 1-indexed).
Example 1:
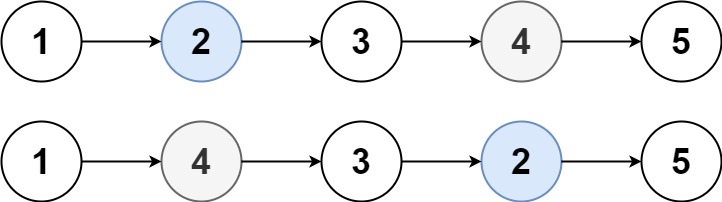
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [1,4,3,2,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [7,9,6,6,7,8,3,0,9,5], k = 5 Output: [7,9,6,6,8,7,3,0,9,5]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
n. 1 <= k <= n <= 1050 <= Node.val <= 100
Code
One pass
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* swapNodes(struct ListNode* head, int k) {
struct ListNode* front = head;
struct ListNode* runner = head;
struct ListNode* back = head;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
front = runner;
runner = runner->next;
}
while(runner) {
back = back->next;
runner = runner->next;
}
int temp = front->val;
front->val = back->val;
back->val = temp;
return head;
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapNodes(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode* front = nullptr, *back = nullptr;
for(auto p = head; p != nullptr; p = p->next) {
back = back == nullptr ? nullptr : back->next;
if(--k == 0) {
front = p;
back = head;
}
}
swap(back->val, front->val);
return head;
}
};