Description
There are n servers numbered from 0 to n - 1 connected by undirected server-to-server connections forming a network where connections[i] = [ai, bi] represents a connection between servers ai and bi. Any server can reach other servers directly or indirectly through the network.
A critical connection is a connection that, if removed, will make some servers unable to reach some other server.
Return all critical connections in the network in any order.
Example 1:
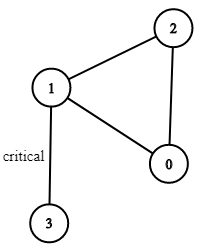
Input: n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[1,3]] Output: 1,3 Explanation: 3,1 is also accepted.
Example 2:
Input: n = 2, connections = 0,1 Output: 0,1
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 105n - 1 <= connections.length <= 1050 <= ai, bi <= n - 1ai != bi- There are no repeated connections.
Code
Tarjan’s Algorithm
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
class Solution {
vector<vector<int>> adj;
vector<vector<int>> res;
int time = 0;
public:
vector<vector<int>> criticalConnections(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
adj.resize(n);
for(auto conn: connections) {
adj[conn[0]].emplace_back(conn[1]);
adj[conn[1]].emplace_back(conn[0]);
}
vector<int> visited(n, 0);
vector<int> parent(n, -1);
vector<int> dfn(n, 0);
vector<int> low(n, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(!visited[i]) dfs(i, visited, dfn, low, parent);
}
return res;
}
void dfs(int u, vector<int>& visited, vector<int>& dfn, vector<int>& low, vector<int>& parent) {
visited[u] = 1;
dfn[u] = low[u] = time++;
for(int v: adj[u]) {
if(v == parent[u]) continue;
if(!visited[v]) {
parent[v] = u;
dfs(v, visited, dfn, low, parent);
if(low[v] > dfn[u]) res.push_back({u, v});
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
} else {
low[u] = min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
}
}
};