Description
Given an array of integers heights representing the histogram’s bar height where the width of each bar is 1, return the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.
Example 1:
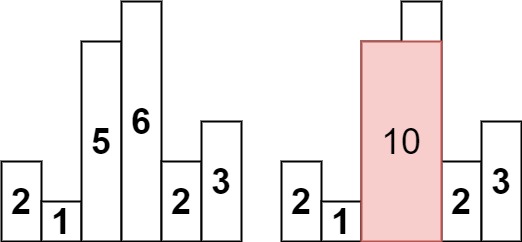
Input: heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3] Output: 10 Explanation: The above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1. The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area = 10 units.
Example 2:
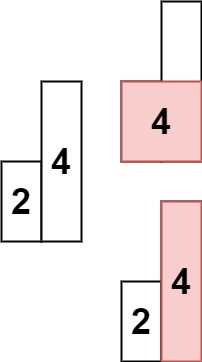
Input: heights = [2,4] Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= heights.length <= 1050 <= heights[i] <= 104
Code
Two Pointer
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
l_cliff 和 r_cliff 紀錄的是往左往右第一個比自己矮的 index,因為對於一個 bar 來說,可以形成的最大 rectangle 就是用自己的 height 往左往右開始延伸,遇到比自己矮的再停下來。比自己矮的不需要在這時候計算,因為當這個矮的自己當成基準時,就會算到他了。
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& height) {
int n = height.size();
vector<int> l_cliff(n, 0), r_cliff(n, 0);
l_cliff[0] = -1;
r_cliff[n - 1] = n;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int p = i - 1;
while(p >= 0 && height[p] >= height[i]) {
p = l_cliff[p];
}
l_cliff[i] = p;
}
for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
int p = i + 1;
while(p < n && height[p] >= height[i]) {
p = r_cliff[p];
}
r_cliff[i] = p;
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res = max(res, height[i] * (r_cliff[i] - l_cliff[i] - 1));
}
return res;
}
};Monotonic Stack
Time Complexity: , Space Complexity:
當 Monotonic Stack 在 pop 時,就是 Two Pointer 中的 r_cliff,而 int idx = s.empty() ? -1 : s.top(); 就是 l_cliff。
要注意用 height.push_back(0); 去處理最後一段嚴格遞增。
因為 monotonic stack 是嚴格遞增,因此在 pop stack 時,一路往左,寬度增加但是高度下降。也因為要維持嚴格遞增,因此遇到高度比目前 stack top 高度還低時,要先 pop,反正這根比較矮的 bar 會在之後它自己被 pop 時去計算它所能構成的 max rectangle area(edge case: height.push_back(0);)。
關鍵在於 int idx = s.empty() ? -1 : s.top();。
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& height) {
stack<int> s;
height.push_back(0);
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < height.size(); i++) {
while(!s.empty() && height[s.top()] >= height[i]) {
int h = height[s.top()];
s.pop();
int idx = s.empty() ? -1 : s.top();
int area = h * (i - idx - 1);
res = max(res, area);
}
s.push(i);
}
return res;
}
};