Description
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return true if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals targetSum.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
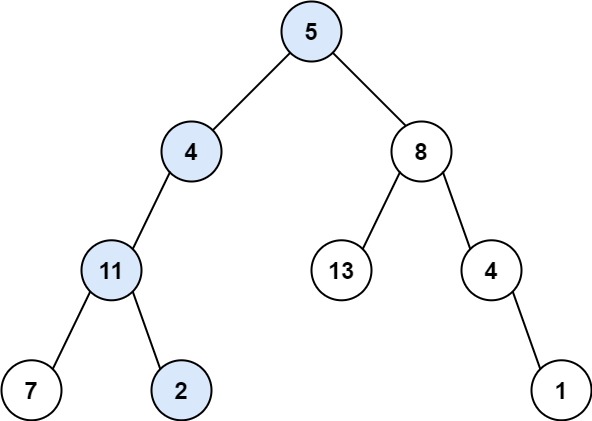
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 Output: true Explanation: The root-to-leaf path with the target sum is shown.
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 Output: false Explanation: There two root-to-leaf paths in the tree: (1 → 2): The sum is 3. (1 → 3): The sum is 4. There is no root-to-leaf path with sum = 5.
Example 3:
Input: root = [], targetSum = 0 Output: false Explanation: Since the tree is empty, there are no root-to-leaf paths.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
Code
要 check left & right child,兩個都是 nullptr 才算是 leaf node。不能只 check 一邊。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(!root) return false;
if(!root->left && !root->right) {
if(targetSum == root->val) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
targetSum -= root->val;
return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum);
}
};