What
Why
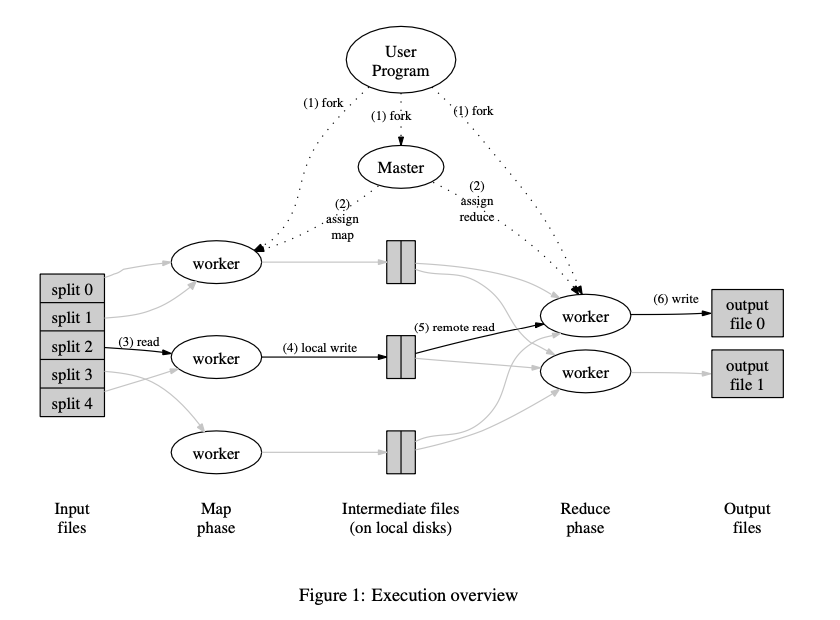
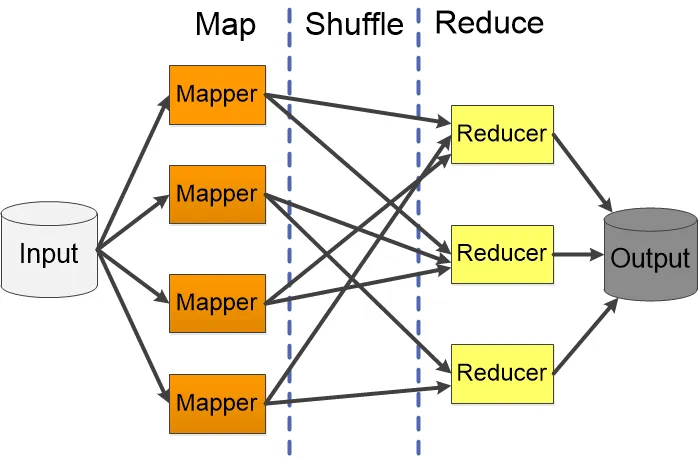
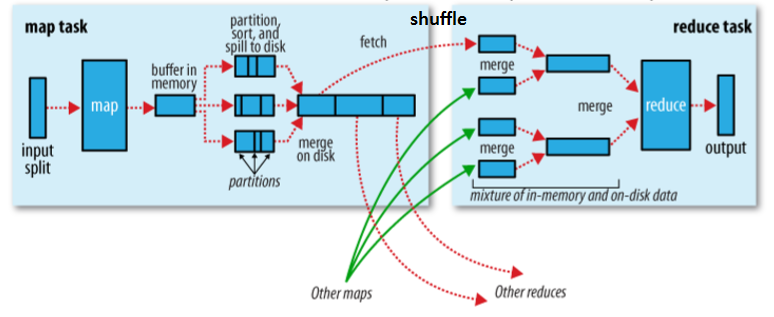
How
map (k1,v1) -→ list(k2,v2)
reduce (k2,list(v2)) -→ list(v2)
serialization and deserialization Iterator → Lazy Load
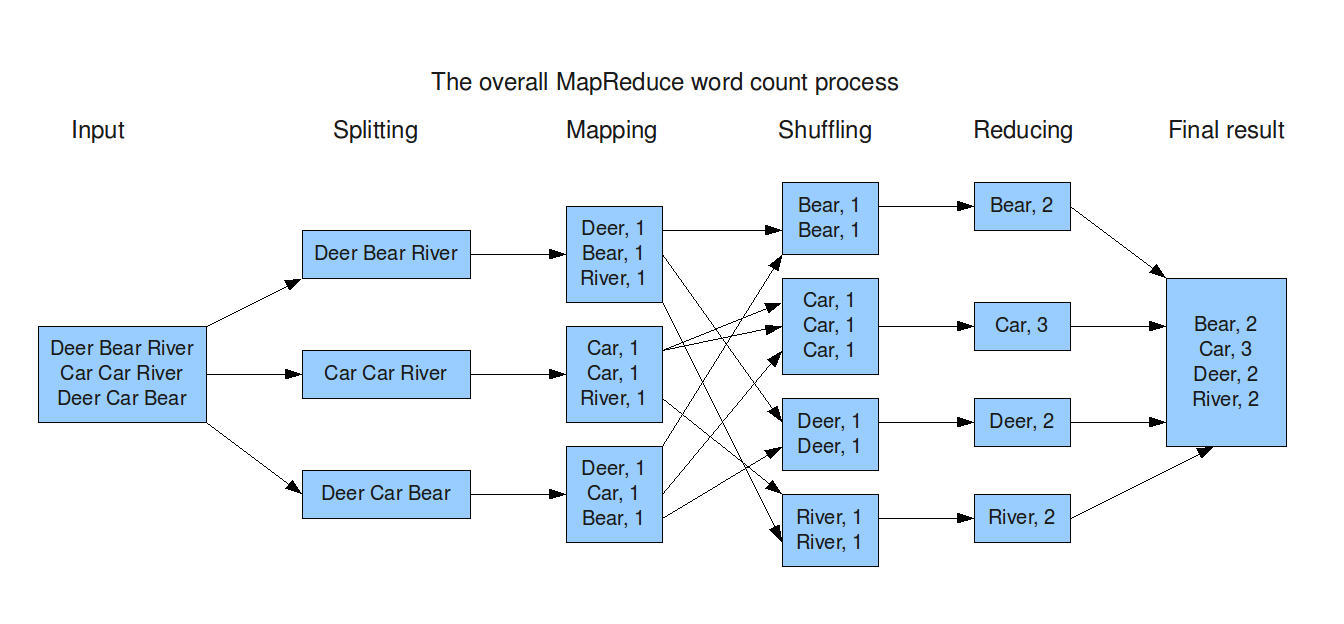
A Toy Example
map(String key, String value):
// key: document name
// value: document contents
for each word w in value:
EmitIntermediate(w, "1");
reduce(String key, Iterator values):
// key: a word
// values: a list of counts
int result = 0;
for each v in values:
result += ParseInt(v);
Emit(AsString(result));
# Map function
def map(key, value):
# key: input split ID
# value: text content of the split
for word in value.split():
emit(word, 1)
# Reduce function
def reduce(key, values):
# key: word
# values: list of counts for the word
emit(key, sum(values))Successors to MapReduce at Google
-
FlumeJava
- A high-level API for writing data processing pipelines in Java.
- It simplifies the creation of complex data pipelines and can execute them using MapReduce or other backend engines.
-
Dataflow (Apache Beam)
- A unified model for both batch and stream processing.
- Google Cloud Dataflow is the managed implementation, providing scalability and performance.
- Apache Beam (open-source) allows the same code to run on multiple engines like Flink, Spark, or Google Cloud Dataflow.
-
Spanner and F1
- Spanner is a globally distributed database designed for consistency and scalability.
- F1, Google’s successor to Bigtable, is built on Spanner and optimized for large-scale relational queries.
-
Dremel (BigQuery)
- A distributed query engine that powers Google’s BigQuery.
- It supports low-latency, ad-hoc SQL queries on petabytes of structured data.
Industry Perspective
Google’s departure from MapReduce mirrors a broader industry trend. Modern distributed systems often favor:
- Real-time and stream processing systems (e.g., Apache Kafka, Apache Flink).
- Declarative big data frameworks (e.g., Apache Spark, Hive on Tez).
Frameworks like Apache Spark, which offers in-memory computation and better abstractions, have gained wide adoption in the industry and overshadowed MapReduce.