Description
You are in a city that consists of n intersections numbered from 0 to n - 1 with bi-directional roads between some intersections. The inputs are generated such that you can reach any intersection from any other intersection and that there is at most one road between any two intersections.
You are given an integer n and a 2D integer array roads where roads[i] = [ui, vi, timei] means that there is a road between intersections ui and vi that takes timei minutes to travel. You want to know in how many ways you can travel from intersection 0 to intersection n - 1 in the shortest amount of time.
Return the number of ways you can arrive at your destination in the shortest amount of time. Since the answer may be large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
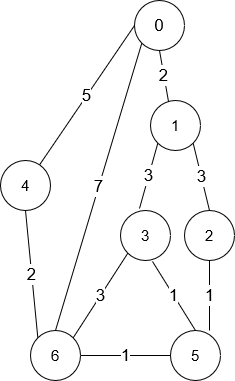
Input: n = 7, roads = [[0,6,7],[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[1,3,3],[6,3,3],[3,5,1],[6,5,1],[2,5,1],[0,4,5],[4,6,2]] Output: 4 Explanation: The shortest amount of time it takes to go from intersection 0 to intersection 6 is 7 minutes. The four ways to get there in 7 minutes are:
- 0 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 4 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 2 ➝ 5 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 3 ➝ 5 ➝ 6
Example 2:
Input: n = 2, roads = 1,0,10 Output: 1 Explanation: There is only one way to go from intersection 0 to intersection 1, and it takes 10 minutes.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 200n - 1 <= roads.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2roads[i].length == 30 <= ui, vi <= n - 11 <= timei <= 109ui != vi- There is at most one road connecting any two intersections.
- You can reach any intersection from any other intersection.
Solution
Dijkstra’s Algorithm 的正確性以及為何只適用 edge weight > 0 的 graph 可以參考:Correctness of Dijkstra_s Algorithm。
這題題幹敘述看完就知道是要我們用 Dijkstra’s Algorithm 來解。
要思考的點是當 path cost 相同時,ways 的更新方式:當發現有另外一條 path 其 cost 和原本相等,則 ways 相加。
Python
class Solution:
def countPaths(self, n: int, roads: List[List[int]]) -> int:
# build adjacency list
adj_list = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v, time in roads:
adj_list[u].append([v, time])
adj_list[v].append([u, time])
# Dijkstra's Algorithm for shortest path on non-negative weight graph
min_heap = [[0, 0]] # time, node
dist = [float('inf')] * n
ways = [0] * n
ways[0] = 1
MOD = 10 ** 9 + 7
while min_heap:
time_taken, node = heappop(min_heap)
# Ignore outdated heap entries
if time_taken > dist[node]:
continue
for neighbor, time in adj_list[node]:
new_time = time_taken + time
if new_time < dist[neighbor]:
dist[neighbor] = time_taken + time
ways[neighbor] = ways[node] % MOD
heappush(min_heap, [new_time, neighbor])
elif new_time == dist[neighbor]:
ways[neighbor] += ways[node]
ways[neighbor] %= MOD;
return ways[n - 1]C++
也可以考慮使用 multiset,可以先 delete 再 insert 來達成 update 的目的。
priority_queue
typedef pair<long long, long long> pa;
class Solution {
public:
int countPaths(int n, vector<vector<int>>& roads) {
int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
vector<vector<pa>> adj(n);
// min heap
priority_queue<pa, vector<pa>, greater<>> pq;
for(auto road: roads) {
adj[road[0]].push_back({road[1], road[2]});
adj[road[1]].push_back({road[0], road[2]});
}
vector<long long> dist(n, LONG_MAX);
vector<long long> ways(n);
ways[0] = 1;
dist[0] = 0;
pq.push({0, 0}); // dist, src
while(!pq.empty()) {
auto [d, u] = pq.top(); pq.pop();
if(d > dist[u]) continue;
for(auto [v, time]: adj[u]) {
if(dist[v] > d + time) {
dist[v] = d + time;
pq.push({dist[v], v});
ways[v] = ways[u];
} else if(dist[v] == d + time) {
ways[v] = (ways[v] + ways[u]) % MOD;
}
}
}
return ways[n-1];
}
};Multiset
typedef pair<long long, long long> pa;
class Solution {
public:
int countPaths(int n, vector<vector<int>>& roads) {
int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
vector<vector<pa>> adj(n);
multiset<pa> min_heap;
for(auto road: roads) {
adj[road[0]].push_back({road[1], road[2]});
adj[road[1]].push_back({road[0], road[2]});
}
vector<long long> dist(n, LONG_MAX);
vector<long long> ways(n);
ways[0] = 1;
dist[0] = 0;
min_heap.insert({0, 0}); // dist, src
while(!min_heap.empty()) {
auto [d, u] = *min_heap.begin();
min_heap.erase(min_heap.begin());
for(auto [v, time]: adj[u]) {
if(dist[v] > d + time) {
if(min_heap.find({dist[v], v}) != min_heap.end()) {
min_heap.erase(min_heap.find({dist[v], v}));
}
dist[v] = d + time;
min_heap.insert({dist[v], v});
ways[v] = ways[u];
} else if(dist[v] == d + time) {
ways[v] = (ways[v] + ways[u]) % MOD;
}
}
}
return ways[n-1];
}
};